Pharma and Healthcare
Pharmaceutical counterfeiting, tampering, and diversion—the three biggest threats to the integrity of the global drug supply—are escalating. The advent of inexpensive and sophisticated imaging technologies and the growth of Internet sales and distribution channels provide criminals with the means to make convincing fakes with little training or capital. The high prices and brand recognition commanded by well-known drugs provide motives for criminals to shift their business away from trafficking in street drugs, which can be less profitable and riskier, to fake‘legitimate’ drugs. Aside from undermining the profitability and brand integrity of major companies, pharmaceutical fraud has the potential to contribute to a world health crisis, endangering the lives of millions of people who rely on the authenticity of prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) drugs.
Fighting the Problem
The types of frauds such as counterfeiting, tampering, and diversion demands a new mindset for drug manufacturers and regulators alike: they must recognize the need to treat pharmaceutical packaging like a valuable currency, and secure it with robust security and authentication features.
The Solution
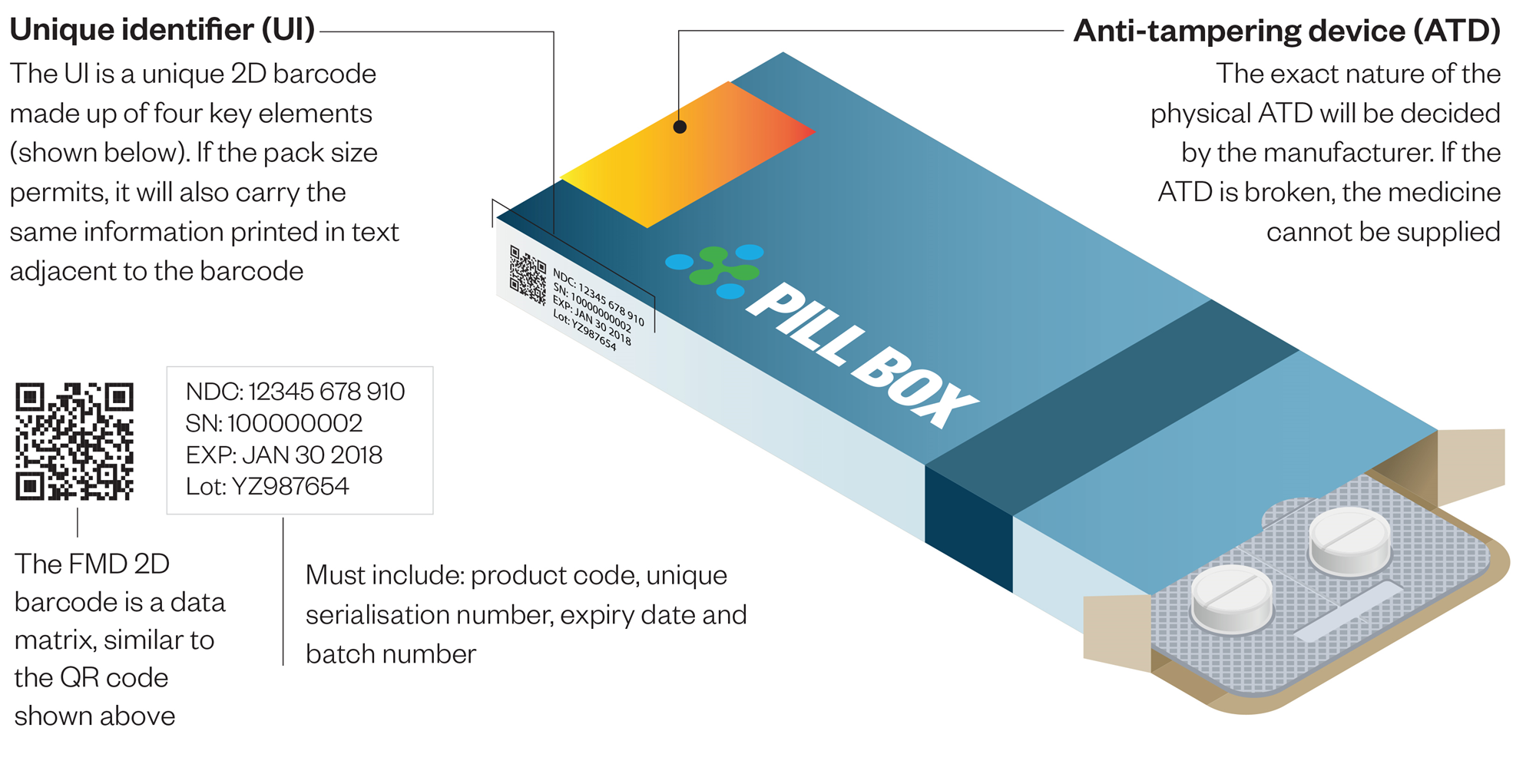
To generate the best solution, authentication solution providers should use ISO 12931 to consider all appropriate technologies and match the best features and techniques with their customers’ particular challenges. In many cases, only a combination of technologies will meet customer requirements. While it is difficult to establish specific rules across various challenges and issues, strategies that incorporate an amalgamation of overt, covert, and forensic security technologies provide the most functionality to deliver the optimal level of authentication.An ideal solution must include a phygital solutions providing authentication and supporting traceability (see figure: FMD directive)
Layers of Security
The authentication solutions must incorporate overt and tamper-evident, covert, forensic, digital tracking, and analytical features and techniques for multiple layers of authentication.
Overt Technologies
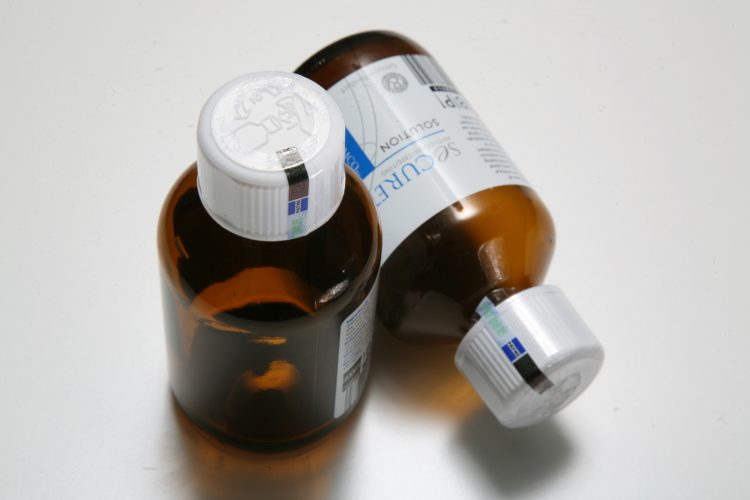
Overt technologies are designed to be easily recognizable but difficult for counterfeiters to replicate. They deliver unique visual features that a consumer can easily validate in a point-of-sale environment with the tools they carry with them every day—their eyes. These features include inks, holograms, labels, and tamper-evident seals and provide the first layer of protection against the fraudulent use of a product
Covert Technologies
Covert technologies contain hidden features that are not visible to the human eye and can only be detected with commercially available microscopes or specialized readers, making them ideal for second level field investigators looking for an added degree of certainty in the authentication process. Covert solutions can be incorporated into products along with overt authentication solutions or can function on a standalone basis to protect against counterfeiting.
A hospital worker concerned about a potential simulation of packaging may not have time to send a questioned drug out for third-party analysis. A covert feature can provide a field investigator (such as a hospital security officer) an additional level of assurance that a product is authentic (or verifiable cause for concern that it is not).
Current technology features a broad spectrum of covert authentication solutions that varies from machine readable technology and micro-text.
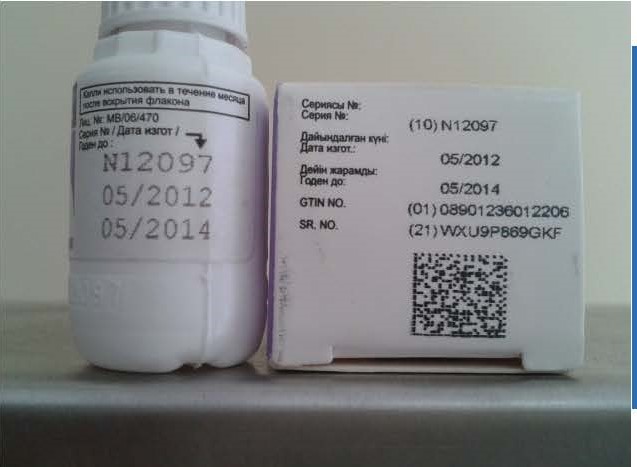
Track-and-Trace Digital Technologies
Digital-authentication solutions provide actionable intelligence to brand owners through electronic means so that they can pinpoint unauthorized sellers on the internet, track-and-trace products through the distribution chain, and remotely authenticate a product anywhere and anytime by scanning a product label with a smartphone or by entering a code into a computer. A robust digital-authentication program can help prevent fake drugs from entering the supply chain, providing a key complement to the benefits of overt and covert technologies.