Counterfeiting - Overview
Introduction
In layman language, the making of an imitation, copy of forgery of a genuine document, card, product, label, or package with the intention to deceive or defraud is counterfeiting. It is a global problem and no economies in world can overruled it. According to International Chamber of Commerce, the global economic value of counterfeiting and piracy could reach $2.3 trillion by 2022.
In the Indian scenario, at present counterfeiting causes around Rs 1.05 lakh crore losses to country per annum. However, the black market by its nature cannot be measured precisely. As the Indian industries are expanding exponentially, so is counterfeiting, so much that it has almost become an industry in itself. The problem is much serious than just a number.
Types of Counterfeiting
In today’s business context, Brands/Products are under attack not just from known or visible competitors but even from invisible enemies in form of product tampering, counterfeiting, and pilfering. Fighting these needs a prolonged strategy and it is important to identify the type & threat of risks prior to selecting or developing effective countermeasures. In most of these cases, fraudsters may not be following the regulatory quality practices of Good manufacturing and hygiene. From the consumers angle, he/she may face counterfeiting in form of deceptive or non-deceptive. While deceptive products are presented as being genuine with intention to deceive the consumer, the non-deceptive counterfeit products are marketed to consumers who seek counterfeit products such as in case for apparel, shoes, and luxury brands. However, directly, or indirectly all these products are harming and impacting all of us (industry, economy, and consumer).
Impact of Counterfeiting
Counterfeit goods impacted everyone. Directly and indirectly, it impacts legitimate manufacturers, exchequer and by large consumer and society.
- Counterfeiting, Tampering, and Diversion Harms Consumer
- Illness or loss of life — Poor quality products especially falsified medicines that are tampered with can cause death and serious illness, as seen in connection with several incidents of counterfeiting in the developing world. The WHO estimates that a fifth of the one million annual deaths from malaria could be prevented if all medicines for it were genuine and taken properly. In Nigeria, 100 children died when a cough medicine was diluted with a poisonous solvent; in Haiti, at least 59 children died after taking counterfeit syrup labeled to treat fever.
- Higher costs for Brands — As a result of lost revenue, exposure to huge damage claims, and higher insurance rates, consumers are faced with higher prices for drugs targeted by counterfeiters and diverters.
- Counterfeiting, Tampering, and Diversion Harms Manufacturer
- Lost revenue — Counterfeit products are made at the direct expense of drug manufacturers who spend millions of rupees developing and promoting their products.
- Liability —Manufacturers can face potentially crippling lawsuits as incidents of counterfeiting, tampering, and diversion pose increasing health and security problems for the public. Plaintiffs hold drug manufacturers accountable for the authenticity of the products they manufacture and the safeguards in place to prevent tampering.
- Brand Integrity — Brands owners / Companies invest huge amounts of resources, time, and money to develop, promote, and maintain their brands. But that investment can be undermined by a single incident or a perception that the product may be fake.
- Counterfeiting, Tampering and Diversion Harms Governments
- Public health crises — Consumption of counterfeit products can cause widespread illness that may overwhelm the healthcare system or create healthcare crises worldwide. According to sources, over 250 people died in India because of hooch tragedies in the year 2019.
- Lost tax revenues — Sales of counterfeit or diverted drugs bypass traditional sales channels, thereby depriving governments of tax revenues.
- Increased enforcement costs — As counterfeiting, tampering, and diversion grow, governments need to allocate a greater portion of their security budgets toward efforts ensuring the integrity of pharmaceuticals.
- Funding of criminal enterprises — The people that benefit most from counterfeiting, tampering, and diversion are criminals who then use their proceeds to fund other criminal activity or to further their own enterprises.
Sectors affected by Counterfeiting
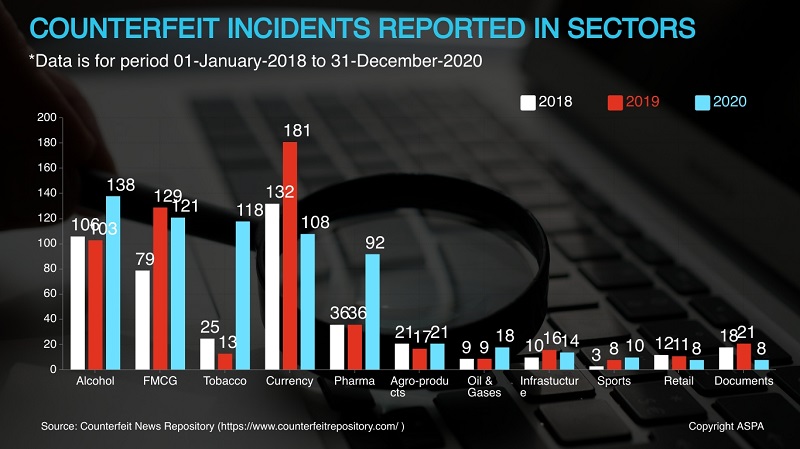
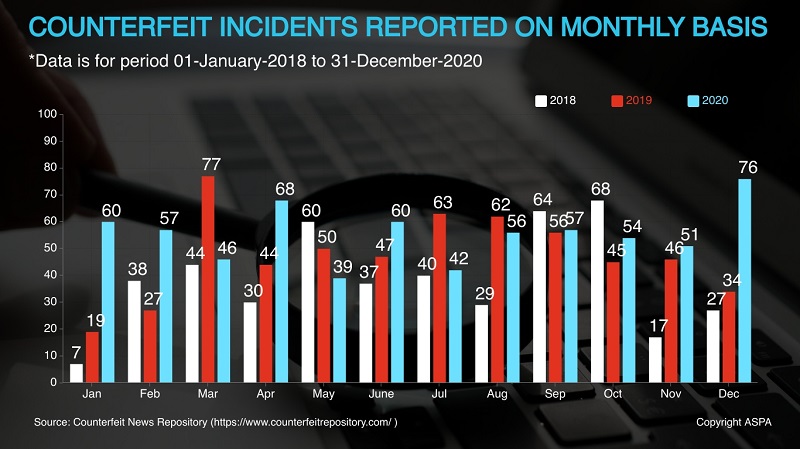
The spread of counterfeiting is far and wide, and ranges from counterfeit automobile and aerospace parts to fake luxury items. The graphics below show the sectors that have been affected the most. Alcohol, Tobacco, FMCG Packaged Goods, Currency & Pharmaceuticals constitutes more than 84% of counterfeit cases. During the COVID-19 lockdown, there was a spike in crimes related to illicit liquor and pharmaceutical products especially PPE kits and sanitizers, etc. Fraudsters have some ingenious methods of producing and smuggling liquor. For example, many people started producing liquor from hand sanitizers.
Counterfeiting Latest Trends
According to the “Study of Counterfeiting in India 2021” there is an increase in counterfeiting incidents from where they were in 2019 and 2018. The number of incidents being reported by media have also surged. In the last three years, counterfeiting incident had increase by 20% between 2018 to 2020. In 2020, 666 cases were reported with an increase of 96 cases comparing to 2019 (570).
In recent years, we have noticed an uptick in ‘unsophisticated’ frauds. Professional fraudsters have been busyadapting to new methods. They are now using the latest manufacturing and printing technologies to duplicate finishes, print boxes, labels, codes, and packaging that mimics genuine products perfectly.
Our data interprets that counterfeiters are targeting both quantity and quality and the highest proportion of cases fall under ‘Easy’ or ‘Medium’, with only an exceedingly small percentage of cases classified as ‘Hard’.
Key reasons for increase
- No specific legislation to address counterfeiting: India has a robust legal framework for combating counterfeiting and piracy, but a lot still needs to be done to simplify the enforcement procedure (as there is no specific legislation to address it). Thankfully, statutory remedies – civil, criminal, and administrative – can be found in various statutes, including the Trademarks Act 1999, the Copyright Act 1957, the Patents Act 1970, the Designs Act, the Geographical Indications Act 1999, the Drugs and Cosmetics Act 1940, the Food Safety and Standards Act 2006, the Consumers Protection Act 1986, the Penal Code, the Information Technology Act 2000, and the Customs Act, 1962.
- Challenges in enforcement and execution: Although a small number of India’s state authorities, including Maharashtra and Telangana, continue to operate dedicated crime enforcement units, other States have not followed suit or face organizational challenges. Further, slow execution encourages the criminals to continue their fraudster activities.
- Non-adoption of technologies leading to identification: Our data shows that in many cases, criminals are acquitted in absence of evidence. As counterfeiters are getting smarter, they can imitate the packaging to a great extent. Many times, in absence of anti-counterfeiting technologies, it becomes difficult for the Police and the Enforcement & Investigative officers to identify the difference between genuine vs. fake, which further results in weak FIR and loopholes in evidence.
- Need clarity on regulations: Pharmaceuticals, Tobacco and Alcohol: The brand owners need to be more aware. Further, it has been often noticed that the adoption of authentication and traceability solutions is exceptionally low in absence of clear regulations. For example, in industries like Pharmaceuticals, Tobacco, and Food, we are yet to implement global authentication and traceability practices and regulations. Plus, there is no mandatory regulation for domestic drugs. We already have serialization for pharma and food exports, and it is important to have consistency in the domestic ecosystem.
Solutions in combating counterfeiting
Fighting counterfeiting is everyone responsibility and need collective effort from all stakeholders. However, the big onus is on Brand Owners and Regulators. The following are some solutions that brand owners, and the government can offer for checking counterfeiting:
By Brand Owners
As brands are under attack, right from manufacturing plant to customers’ place of purchase in form of tamper, theft or replacement that results in bad image and loss of profit, there is a need for integrated approach from the owners of the brands.CEO to take charge/Responsibility: As a first step, every CEO or brand owner should take the responsibility for brand attack and make Brand Risk Management (BRM) a part of his business planning, reviewing and reporting.- CEO to take charge/Responsibility: As a first step, every CEO or brand owner should take the responsibility for brand attack and make Brand Risk Management (BRM) a part of his business planning, reviewing and reporting.
- Building an Integrated Solution: The team should make a customized, totally integrated solution by increasing the participation of co-opting consumers, channel partners and conducting verification, raids orstrong law enforcement.
- Use of Technology: Brand owners should use anti-counterfeiting devices comprising of overt, covertand forensic security features. While there are many technologies a brand manager can use, it isbetter if he chooses his tools at an early stage with some basic guidelines. For more information, on physical and digital authentication solutions, visit the authentication section.
- By Government
- Amendment in Company Law – Brand Risk Management should be treated as part of risk management under Corporate Social responsibility – As an initial step, the governmentcan make it mandatory for every company to incorporate BRM as part of their annual report inwelfare of stakeholders. ‘Brand Risk Management’ should be treated as part of risk management under thedirect responsibility of board of directors/brand owners.
- Consumer education: in India Govt can start such program at management institutes and Universities educating the youth, marketing students, consumers andBrand manager the ill effects of counterfeiting and importance of Brand Protection. Educatingconsumers can play off. For example, the success of IACC college outreach campaign in which students at US universities were educated about the issues associated with counterfeiting.
Conclusion
Fighting counterfeiting is a brand issue, which, when managed well, will result in the following:
- Consumers getting good products at value price.
- Higher market share for manufacturers, increase in brand value and profits.
- Increased revenue for government which can further be used for betterment of society.
- Drying up of one channel for terrorism funding.
The negative impact of counterfeiting can be diminished to a great extent if it becomes a part of every brand’s planning and reviewing process.