Authentication
Overview
Counterfeiting activities are impacting socio-economic development across the globe and becoming one of the critical hindrances to achieving sustainability goals target set by UNO. Including removal of poverty, education to all, etc. etc. A global menace, the problem of this magnitude cannot be solved overnight; perhaps, a preventive step is what we need.
With the advancement of desktop publication & smart scanning technologies, it is becoming easy for counterfeiters to replicate product labelling. The problem is the further aggravated in absence of awareness amongst stakeholders and requires an integrated Anti-Counterfeiting proactive approach from all agencies. Even an expert cannot identify the difference between fake vs. genuine products.
In this scenario, authentication technologies have played an essential role in combating counterfeiting. Every industry and product have their needs, not only regarding the levels of security the solution offered but also their economic viability.
Authentication &Types of Technologies
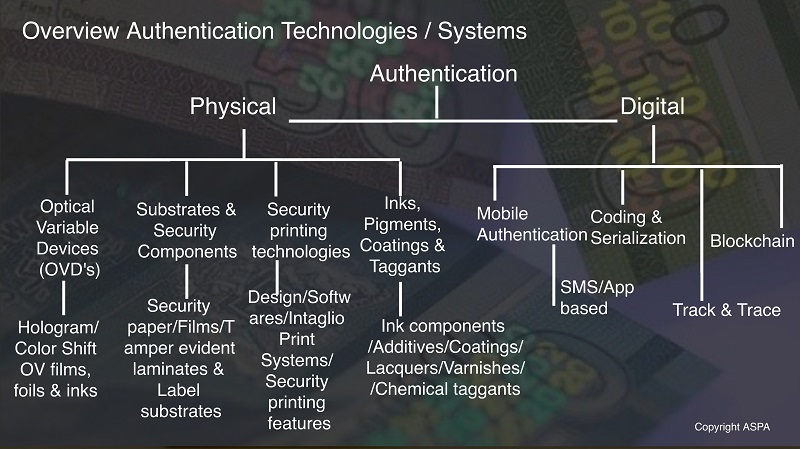
In general terms, Authentication can be defined as, the process of providing that packaging, product, or other item is (or is not) genuine. Generally divided into digital authentication (codes, databases, transaction history, etc.) and sensory authentication (holograms, inks, taggants, etc.).
Today, there are various number of authentication technologies available in the market, although all these technologies are applicable and provide protection in the three main areas.
- Anti-Counterfeiting: The common feature of anti-counterfeiting technologies is that they are extremely difficult to counterfeit. Consequently, they help in identifying a genuine product. Based on the authentication requirements, such technologies may consist of overt, covert and forensicfeatures, or a mix thereof.
- Anti-Tampering: Such solutions are found more in the food and pharmaceutical industry where there is a need to protect a product from adulteration or replacement. An intact anti-tampering feature is the consumers’ assurance that the contents are genuine and not tampered or adulterated.
- Track and Trace: Track and trace technologies use mass serialization to provide a unique identity to each SKU. The IT technology then allows tracking on each SKU through customized software that allows an authorized user to track the movement of this SKU across the entire supply chain. As authorized, each user may also be able to access additional information about the product such as manufacturing date and factory, expiry date, the market such SKU is for etc.
Levels of Authentication Technologies
According to inspection level (human / tools), these technologies fall into categories, either overt, covert, forensic or digital.
- Overt: Overt technologies are authentication devices built into labels, documents and packaging which are visible to the user and show dynamic visual effects. Their main advantage is the fast and easy, on the spot, visual authentication where no additional devices are needed.
Overt features fulfil three main criteria.
– Communicate with the verifier
– Be easy to identify
– Be hard to copy and imitatePhysical secure solutions offering overt features include Fine line design, security guilloches, holograms, optically variable devices (OVDs), watermarks, colour-shift and thermochromic inks, threads, foils, and laminates, embossable and laser markable films and security papers.
Overt features can be made more secure by combining them with covert, forensic and digital features. As Overt are used for identification and verification by the consumer, Covert (Verification by a predetermined device or a tool) can be used by the manufacturer or their channel partner for an advanced level of authentication and verification. The third level is highly sophisticated and can be used by forensic experts and can be useful to law enforcement and for evidence in case of litigation.
Mainly classified as overt OVDs technologies security hologram & inks produced in the high-security environment provide covert as well as forensic features.
- Covert: Covert technologies are not instantly recognizable. They require a special reader or detector to be able to verify their presence and validity, and people using covert technologies will normally require training. Covert technologies include ultraviolet and infrared inks, micro text, unique synthetic tagging etc.
- Forensic: Forensic technologies, being covert, are not readily recognisable and require special tools for detection and validation. Whereas covert technologies can be detected and validated in the field, forensic technologies must often be taken to a laboratory with specialised equipment.
- Digital: Digital technologies may be either overt or covert, but all require an electronic means for detection and validation. Digital technologies are most associated with RFID tags or with serialised numbers that can be compared to a remote database.
How to select an ideal technology?
There are various anti-counterfeiting technologies available, and you can identify the best fit according to your requirements. One can also take reference from other industries guidelines and advisory.
As an additional step, the Alcohol brand owner / authorities can also adopt a new ISO Standard titled, “ISO 1293:2012 Performance criteria for authentication solutions used to combat counterfeiting of material goods”. This is an extremely useful standard for a brand owner wishing to adopt globally accepted good business practice and systems to fight the menace of counterfeiting. This can be seen at http://www.iso.org/iso/catalogue_detail?csnumber=52210.
In ideal conditions, the solutions must be a combination of physical + digital technology. While physical must ensure tamper resistance, digital will provide real time data intelligence, transparency, and traceability. One should always focus on solutions rather than relying solely on specific individual technology.
If you are using a security hologram, you must register it with IHMA Hologram Image Register operated by Counterfeit Intelligence Bureau (CIB). ASPA has an arrangement with them so that its members can register their security hologram with CIB. The hologram industry is the only authentication technology that keeps a database of the security images produced by the industry. The selection and proper implementation of the right technologies will invariably lead to long term benefits to the brand owner. More information can be access with link https://www.ihma.org/image-register.aspx
Evaluation parameters of authentication solutions provider (vendor)
The selection of a vendor is particularly important. In a bid to ensure selection and success of technology solutions in tackling counterfeit, a brand owner must select a vendor willing to sign NDA, follow written ethical policy. The vendor should have experience & technology strengths and be a member of Anti-Counterfeiting Trade Bodies such as Authentication Solution Providers’ Association (ASPA) / International Hologram Manufacturers Association (IHMA) / INTERGRAF / International Tax Stamp Association (ITSA) members. He must not be a trader and ready for audit of its facilities.
Ideal Anti-counterfeiting Strategy
While technology’s role is critical in combating counterfeiting, the complete Anti-Counterfeiting Strategy needs to go beyond that. Counterfeiters are becoming successful because we are not making their task difficult or in another way, we are not making this business less profitable for them. In most of the cases, the product packaging was easily copied due to availability of packaging raw materials in neighboring countries/geographies. Further, non-adoption of authentication solutions, inadequate surveillance efforts by brand owners to identify counterfeit products and lack of consumer awareness is helping them.
An ideal Anti-Counterfeiting Strategy must have key elements including:
- Correct diagnosis or Risk Assessment
- Identifying Right Brand protection partner / vendor
- Selection of Solutions
- Data intelligence and enforcement
- Brand & Consumer engagement in building Authentication ecosystem
Policies ensuring implementation of active anti-counterfeiting measures across sectors can bring a huge turnaround for the economy by contributing to the revenues of both the government and businesses. This considerable amount of added government revenue can be invested towards schemes for citizen wellbeing such as education and health. Even at time of any crisis, the authentication and traceability become important tools in identifying & calculating the real time demand and supply chain information.
For more information, understanding physical authentication solutions, click here
For more information, understanding digital authentication solutions, click here
For more information, on selecting authentication solutions, click here